How To Solve For Kb

Equilibria of Weak Bases, Kb
- What is a weak base?
- Calculating Kb
- Calculating equilibrium concentraions in an aqueous solution of a weak base
A weak base is any base that reacts with water (accepts H+ ions) to a very small extent, usually less than 5 - 10%. An aqueous solution of a weak base in a state of equilibrium would consist mainly of the unionized form of the base, and only a small amount of hydroxide ions and of the cation (conjugate acid) of the weak base. The equation representing the ionization of any weak acid, B, and the equilibrium expression, Kb, are shown below.
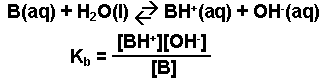
Note: This expression, Kb, is based on the general form for Kc. The designation Kb is used to indicate that it is the equilibrium constant for the reaction of a base with water.
Top
Calculating Kb
To calculate the ionization constant, Kb, you need to know:
- the equation for the reaction of the base with water
- the equilibrium expression, Kb, for the reaction
- the equilibrium concentration of each species (molarity or moles per liter) or have a means to obtain them
Example: The pH of a 0.1000 M solution of aniline solution was found to be 8.79. Determine the value of Kb, the ionization constant for aniline. The formula for aniline is C6H5NH2.
- Write the equation for the reaction of the aniline with water.
C6H5NH2(aq) + H2O(l)
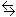 C6H5NH3 +(aq) + OH-(aq)
C6H5NH3 +(aq) + OH-(aq) - Write the equilibrium expression for the reaction.
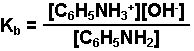
- Convert the pH of the solution into pOH, and then into the hydroxide ion concentration. This will be the equilibrium concentration of the hydroxide ion.
pOH = 14 - pH = 14 - 8.79 = 5.21
[OH-] = 10-pOH = 10-5.21 = 6.17 x 10-6 M
- Make an ICE chart to aid in identifying the variables. The hydroxide ion concentration in pure water is 1 x 10-7 M which can be considred as being approximately zero.
C6H5NH2(aq) C6H5NH3 +(aq) OH-(aq) Initial Concentration (M) 0.1000 0 ~ 0 Change in Concentration (M) - 6.17 x 10-6 + 6.17 x 10-6 + 6.17 x 10-6 Equilibrium Concentration (M) ~ 0.1000 6.17 x 10-6 6.17 x 10-6 For explanation of the significance of the different colors click HERE.
- Substitute the equilibrium concentrations into the equilbrium expression and solve for Kb.
Top
Calculating the Equilibrium Concentrations in an Aqueous Solution of a Weak Base
To calculate the equilibrium concentrations you need to know:
- The equation for the reaction of the base with water.
- The equilibrium expression for the reaction and the value of the equilibrium constant, Kb.
- The initial concentration of the base expressed in moles per liter.
- Make an ICE chart. Express the change in equilibrium concentrations for each species in terms of a variable "x".
- Substitute the expressions for the equilibrium concentration into the equilibrium expression and solve for "x".
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration for each species by substituting in the value for "x" and solving.
- Write the equation for the reaction of the base with water.
NH3(aq) + H2O(l)
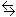 NH4 +(aq) + OH-(aq)
NH4 +(aq) + OH-(aq) - Write the equilibrium expression for the reaction.
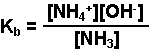
- Make an ICE chart to aid in the solution of the problem. Let "x" represents the change in the concentration of the NH4 + and OH-.
NH3(aq) NH4 +(aq) OH-(aq) Initial Concentraion (M) 0.1000 0 ~ 0 Change in Concentration (M) - x + x + x Equilibrium Concentration (M) 0.1000 - x 0 + x 0 + x For explanation of the significance of the different colors click HERE.
- Substitute the expressions for the equilibrium concentration into the equilibrium expression and solve for "x".
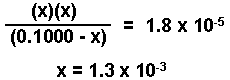
Solved using method of approximations or the quadratic equation.
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration for each species.
[NH4 +] = x = 1.3 x 10-3 M
[OH-] = x = 1.3 x 10-3 M
[NH3] = 0.1000 - x = 0.0987 M
Top

How To Solve For Kb
Source: https://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/howtosolveit/Equilibrium/Weak_Bases.htm
Posted by: landissclows1999.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Solve For Kb"
Post a Comment